Content
1. Why do you need to clean PE pipes?
The cleaning of PE pipes is divided into internal cleaning and external inspection and cleaning.
(1) The main reasons for internal cleaning:
Microbial growth (biofilm): Especially in water supply and water transmission systems, natural microorganisms in the water (such as bacteria and algae) will adhere to the pipe wall and form a layer of biofilm. This film will pollute the water quality, produce odor, and even corrode the pipe wall.
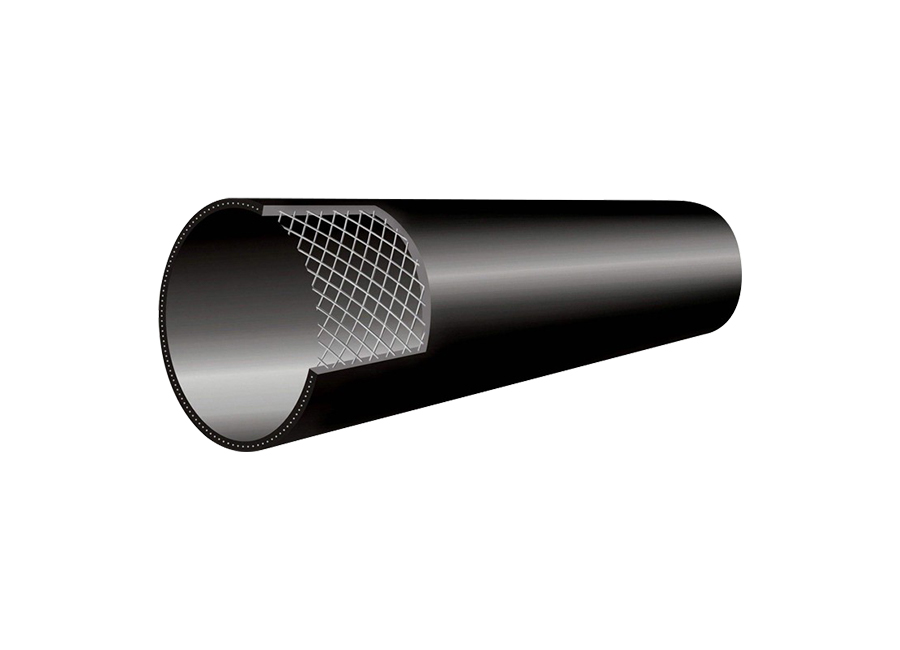
Impurity deposition: Although PE pipes are smooth and not easy to scale, mud, rust, suspended matter, etc. in the water or fluid will still be deposited in areas with low flow rate, reducing the effective diameter of the pipe, increasing the transmission resistance, and reducing the flow rate.
Medium residue: In the chemical or food industry, when changing the transmission medium, if the previous and subsequent media are incompatible, the pipe must be thoroughly cleaned to prevent cross contamination.
(2) The main reasons for external inspection and cleaning:
Check for damage: Cleaning the outer wall of the pipe can easily check for scratches, cracks, extrusion deformation, or signs of leakage at the joints.
Prevent external corrosion: Although PE is resistant to chemical corrosion, it will age if exposed to ultraviolet rays (sunlight) for a long time. After cleaning, it is easy to check its aging status. At the same time, the soil around the buried PE pipe may also pose a threat if it contains sharp stones or specific chemicals.
2. How to clean PE pipes?
(1) Physical cleaning method
High-pressure water jet cleaning:
Principle: Use a high-pressure pump to generate high-pressure water, spray it through a special nozzle, and use the huge impact force of the water flow to flush and cut off the attachments on the pipe wall.
Applicable: Various pipe diameters, especially for sediment deposition and biofilm. It has a good effect. This is the most commonly used and efficient physical method.
PIG pipe cleaning technology (ball cleaning):
Principle: A soft object called a "pipe cleaner" (usually made of polyurethane foam, shaped like a cannonball, commonly known as a "pipe cleaning pig") is placed in the pipe, and the pressure of water or gas is used to push it forward in the pipe, relying on the friction between it and the pipe wall to scrape off dirt.
Applicable: Long-distance pipelines, used to remove sediment and accumulated liquid. The pipeline needs to have a transmitting and receiving device, and there should be no reducers or right-angle elbows.
(2) Chemical cleaning method
Chemical cleaning:
Principle: Inject a specific chemical cleaning agent (such as disinfectant, algaecide, acidic or alkaline cleaning liquid) into the pipeline, and dissolve or kill the biofilm and specific sediments in the pipe through circulating soaking.
Applicable: Situations with serious biofilm and algae pollution, or for disinfection of drinking water pipes.
Important note: After chemical cleaning, the pipeline must be thoroughly flushed with clean water until the water quality test is qualified to ensure that there is no chemical residue. For drinking water pipes, food-grade approved cleaning agents must be used.
3. Cleaning frequency recommendations
Municipal/building water supply pipes: It is recommended to conduct routine inspections and cleaning every 1-2 years, especially when the water quality suddenly deteriorates, the water flow rate is significantly reduced, or after maintenance.
Industrial pipelines: Depending on the characteristics of the conveying medium, cleaning must be carried out before changing the product type or during regular overhauls.
PE pipes for agricultural irrigation: At the beginning and end of each irrigation season, the filter should be checked and cleaned to prevent the dripper from clogging. The main pipeline can be flushed regularly according to the situation.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى